Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are disturbances in the normal rhythmic beating of the heart, causing it to beat too slow (bradycardia) or too fast (tachycardia). These disorders are caused by a problem with the heart’s electrical system involving transmission of electrical signals through the heart muscle via specialized networks which stimulate the heart to squeeze and relax.
Although sometimes arrhythmias occur in a healthy heart and have minimal consequences, they often indicate a serious problem (such as an underlying heart disease) which can result in more serious complications such as stroke or sudden cardiac death. Sudden cardiac death is one of the leading causes of death in the world today.
Advanced technologies and improved understanding of arrhythmias have lead to dramatic advances in the detection and treatment of all types of cardiac rhythm disturbances. We use the most advanced equipment and techniques to provide referring physicians with timely, accurate diagnosis and therapies.
Overview of Arrhythmias
There are various types of arrhythmias which range from benign to those that are of more concern and can have serious clinical consequences.
The most common is atrial fibrillation (AF), AF occurs, the upper chambers of the heart (atria) quiver rapidly and irregularly. AF is typically not life-threatening, but can cause significant quality of life concerns.
A more worrisome arrhythmia that can lead to sudden cardiac death occurs in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). This condition can be effectively treated, but the key challenge is early detection, which involves identifying those who are at risk.
Different types of arrhythmic disorders:
Tachyarrhythmias
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial Flutter
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
Bradyarrhythmias
Sick Sinus Syndrome [Brady-tachy Syndrome] Heart Block (Atrioventricular or “AV” Block)
Genetic/Inherited Heart Rhythm Conditions
- Arrhthmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (ARVD)
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
- Long QT syndrome (LQTS)
- Brugada syndrome
Arrhythmia Evaluation and Diagnosis
A clinical evaluation by the Cardiac Electrophysiologists is the best way to detect irregular heart rhythms early, and manage them before serious problems arise. Some types of arrhythmias can be life threatening, making early diagnosis critical to the prevention of serious problems.
Recognizing signs and symptoms of the condition is an important part of this process. The following are signs and symptoms of irregular heart rhythms:
Signs and Symptoms of Arrhythmias
- Palpitations
- Syncope
Diagnostic Tests
At the Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, evaluation and diagnosis of patients with arrhythmias or suspected arrhythmias includes inpatient and outpatient consultation along with comprehensive diagnostic electrophysiologic testing and intracardiac recording. Tests may include any combination of the following:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram (Echo)[transthoracic and transesophageal]
- Exercise Stress Test
- Holter ECG Monitor
- Event Monitor
- Implantable Loop Recorder
- Cardiac MRI
- Head-Up Tilt-Table Testing
- Electrophysiology Studies (EPS)
Treatment
Medications
Medications remain the front-line treatment for abnormally fast heart rates including atrial fibrillation. Several new medicines are used to stabilize the heartbeat and prevent serious complications by returning the heart to a normal rhythm and, if the arrhythmias continue, there are medications that prevent the heart from beating too quickly.
Non-Surgical Procedures
Implantable Devices
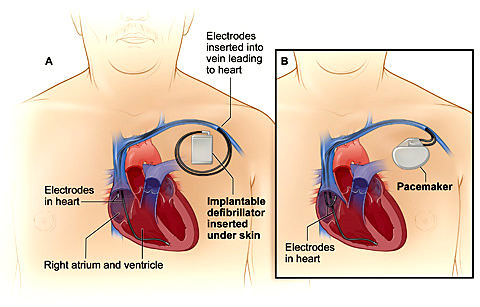
For patients with recurring heart rhythm disturbances, these implantable devices can provide automatic electrical therapy on a continual basis and prevent life threatening arrhythmias. Learn more about the following implantable devices:
- Implantable Cardioverter Device (ICD)
- Pacemaker implantation
- Cardiac Resychronization Therapy (CRT)
- Lead Extraction
Catheter-Based Ablation
Some patients with heart rhythm disturbances (“arrhythmias”) do not respond adequately to treatment with medication, and for other arrhythmia patients, therapy with medications is not as safe or appropriate as more definitive treatment. Catheter ablation is a procedure used to selectively eliminate the heart cells causing the arrhythmia.
Electrical cardioversion
This procedure is used for patients who have persistent atrial fibrillation and involves sending an electrical current through the chest wall to “reset” the heartbeat to a normal rhythm.
Surgical Procedures
Open surgical treatment for arrhythmias is usually done only when all other appropriate options, including minimally invasive surgical procedures, have failed. Surgical ablation is a major surgical procedure requiring general anesthesia. The chest is opened, exposing the heart. The site of the arrhythmia is located; the tissue is destroyed or removed in order to eliminate the source of the arrhythmia. This is typically done at the time of a concurrent cardiac surgical procedure such as cardiac bypass surgery or valve repair/replacement.